Landlocked doesn’t necessarily mean access is lost for good
It would be a mistake to see the results of our latest landlocked study with onX and think that all hope of accessing these lands is lost. In fact, with excellent news coming out of Oregon this week—a strategic land acquisition is helping to open a combined 13,000 acres of public lands to hunters and anglers there—sportsmen and women have a lot to look forward to.
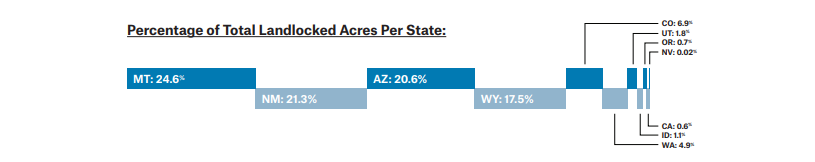
Knowing the full scope of the landlocked problem is one step toward finding the best possible solutions. Here are four ways that Western states are already working to chip away at the 15.8 million landlocked acres that we’ve identified so far.
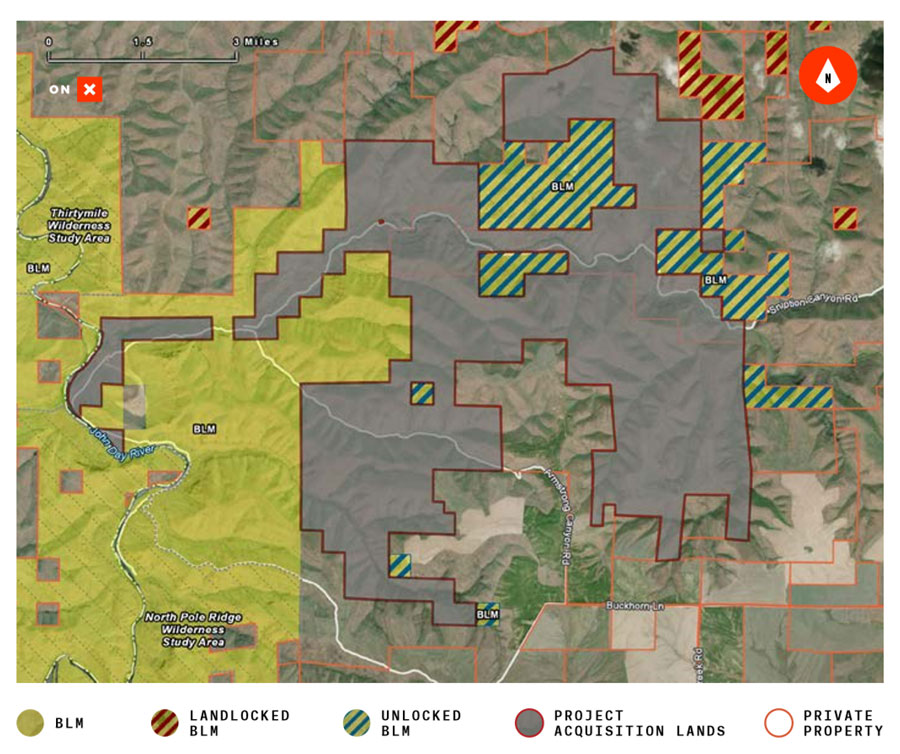
Land Swaps and Smart Acquisitions
Since they received their original land grants, many states have consolidated their trust lands to make them more manageable and profitable. This has been achieved through both land acquisitions and exchanges, whereby the state trades its own lands to another entity for lands in a more desirable location.
Some state natural resource departments have acquired road access easements simply to make it easier to manage previously landlocked parcels. But as access across private lands has become increasingly difficult for sportsmen and women to obtain, these efforts also offer benefits to the public-land hunter or angler.
Now, states have begun to open landlocked state trust lands to public access not just as an ancillary benefit of more streamlined management, but for the expressed purpose of creating more outdoor recreation opportunities. And this is great news for those of us who need more places to hunt and fish close to home.

Dedicated Staff and Programs
One of the most powerful steps a state can take to open landlocked state lands is to assign dedicated staff and/or establish specific programs to address access challenges.
Montana has been a leader on this front, having taken several steps to increase access to state trust lands. While many states have recently created positions focused on serving and expanding outdoor recreation, Montana took the additional step of creating a new role for a public access specialist tasked with expanding access to public lands—both state and federal. This person’s responsibilities include helping the state prioritize and complete access acquisition projects and collaborating with landowners and agency land managers to find common ground around the access issue.
What’s more, the public access specialist has a number of programs at his or her disposal. One such program is the Montana Public Lands Access Network (MTPLAN), which was created by the legislature in 2017 to “facilitate collaboration” and “enhance public access throughout the state.” Through the MTPLAN, the Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation awards grants to eligible groups specifically to acquire public access easements across private lands and open up landlocked or difficult-to-access public lands for recreation.
While the MT-PLAN would benefit from more robust funding, it stands as a praiseworthy effort that other states could follow. And Montana Fish, Wildlife, and Parks has several other programs—including Unlocking Public Lands and the Public Access to Lands Act—that serve to expand access to the state’s 5.2 million acres of trust lands.
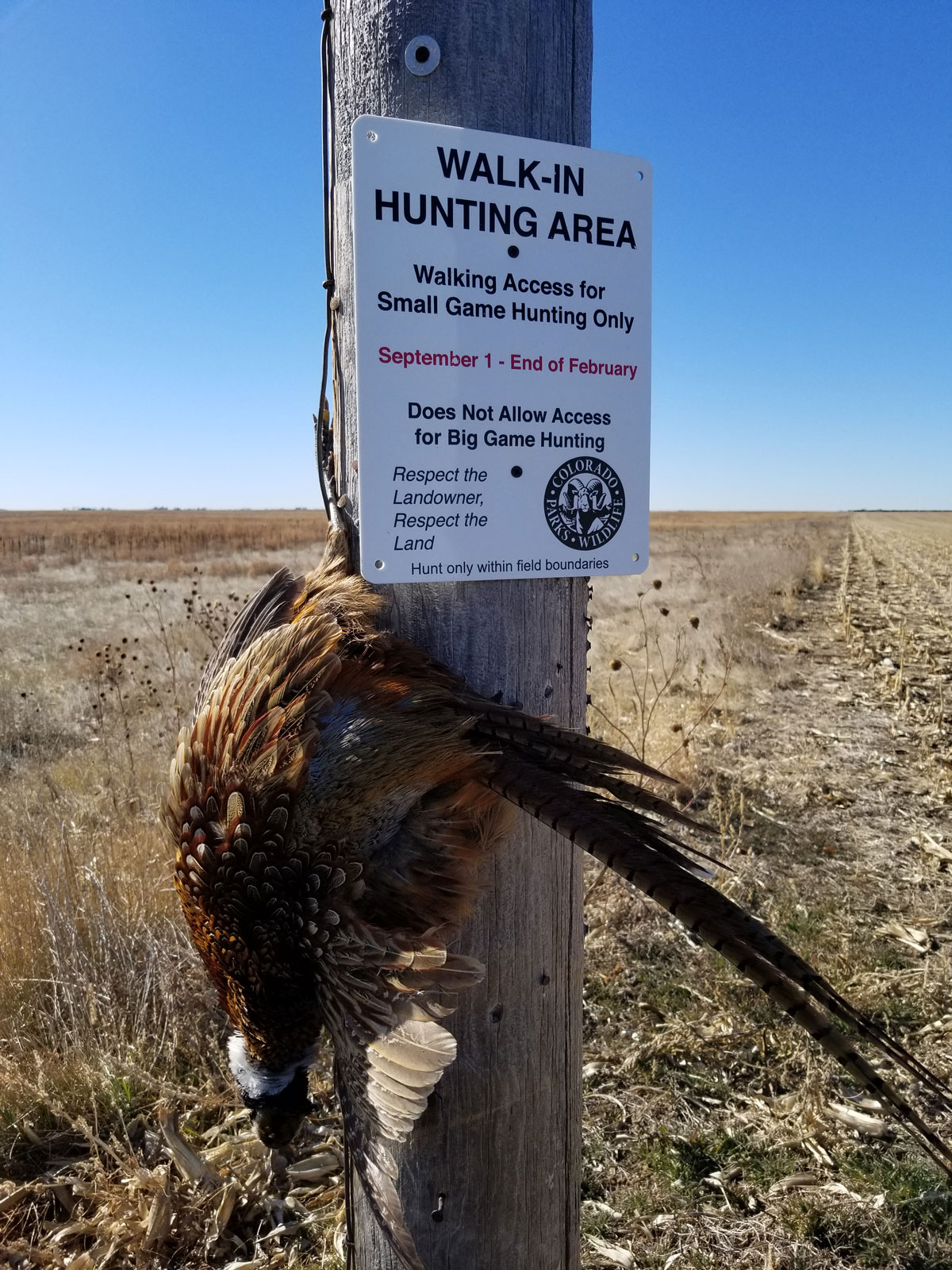

Walk-In Access Programs
Walk-in access programs, such as Idaho’s “Access Yes” and New Mexico’s “Open Gate,” have long been popular with sportsmen and women for their ability to expand hunting opportunities on private lands. These programs are administered by individual state fish and wildlife agencies, which generally enter into short-term contracts with individual private landowners to make their lands available to the public, typically for hunting.
Each program is different, and Nevada is the only state in the Mountain West without one.
Traditionally used only for private land access, state walk-in programs have taken on a new importance as a powerful tool for opening pathways to landlocked state and federal lands. Several states, including Wyoming and Arizona, are deliberately using these programs to open access to landlocked public lands—including state trust lands—by securing leases on private lands that encompass or are adjacent to otherwise inaccessible public lands.
This isn’t a permanent solution, because the access agreements require perpetual renewal, but walk-in programs can be especially valuable in opening smaller and more isolated parcels of state and federal lands that would be difficult or impractical to unlock by any other means. These state programs are generally funded through license dollars or the federal Farm Bill’s Voluntary Public Access and Habitat Incentive Program.
Continued and even increased funding for both sources could be fundamental to supplying more public walk-in access. That means recruiting more license-buying sportsmen and women, supporting R3 efforts, and recognizing the important benefits of VPA-HIP in time for the next farm bill debate.

Using the Land and Water Conservation Fund
We’ve been a bit of a broken record on this one, but can you blame us? According to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, more than 40,000 individual grants and $4.1 billion in LWCF funds have been provided to states and localities to acquire and develop outdoor recreation facilities. And LWCF state dollars—a mandated 40 percent of allocated program funding—can be directed toward unlocking state lands for recreational access right now.
The more funding Congress directs to the LWCF, the bigger chunk of the pie is available to the states, and that’s why we’re pushing for the maximum of $900 million to flow into the LWCF coffers annually, without future quibbling about whether that’s the right amount.
Remember: Oil and gas companies are already handing over $900 million a year for this purpose. But in the past 50 years, more than $20 billion in LWCF funds have been diverted elsewhere.
Support the original promise of the LWCF and the opportunity to unlock inaccessible public lands to which we have every right. Take action now to urge Congress to fully fund this critical access tool.
Top photo by Tom Fowlks.










CONVINCE CONGRESSMEN TO PASS A BILL REQUIRING FED. OFFICIALS TO POLL THE PEOPLE IF PUBLIC LANDS ARE TO BE TRADED, MINED, ROAD BUILDING, ETC. IF THE MAJORITY OF THE PEOPLE SAY NO, THAN THE LANDS ARE LEFT AS IS. REMEMBER, THESE ARE “PUBLIC LANDS” MEANING PEOPLE’S LANDS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Sen Ira Hansen from Nevada put legislation on the books to enforce the Old RR law of the late 1900’s.He notified sheriffs and county DA’s of the new law. This will unlock lots of federally owned hunting areas heretofore reserved to the landowner’s big game guides. Other stTES MIGHT FOLLOW
Here’s another idea–dig for documents. I have found that thousands upon thousands of acres of “landlocked” land has legal access–its just burried in old documents at the court house. Groups like TRCP need to promote funding for a “title search” of landlocked parcels. In Washington state, I have found a goldmine of access to state land by reviewing the wording of easements with private landowers.
The State of Nebraska is becoming a very popular destination for “western hunting” and we currently don’t have the acres of public access available. The state also owns 100,000’s of thousands of acres of “school land” that is state own but not open to public access. Gaining public access to these parcels would be a win to every sportsman across the west. Please consider looking into this and taking the next steps to achieve public access
I am from Montana. As someone that has grown up here and watched more and more access for hunting get swallowed up by wealthy out-of-staters that have the cash to purchase large tracts of land that once were owned by ranching families that allowed access for decades, quickly put a stop to the use. I would like to see a stronger support by our state leadership to give legal access to corner hopping and nailing down historical public land access points before additional acres are lost forever.