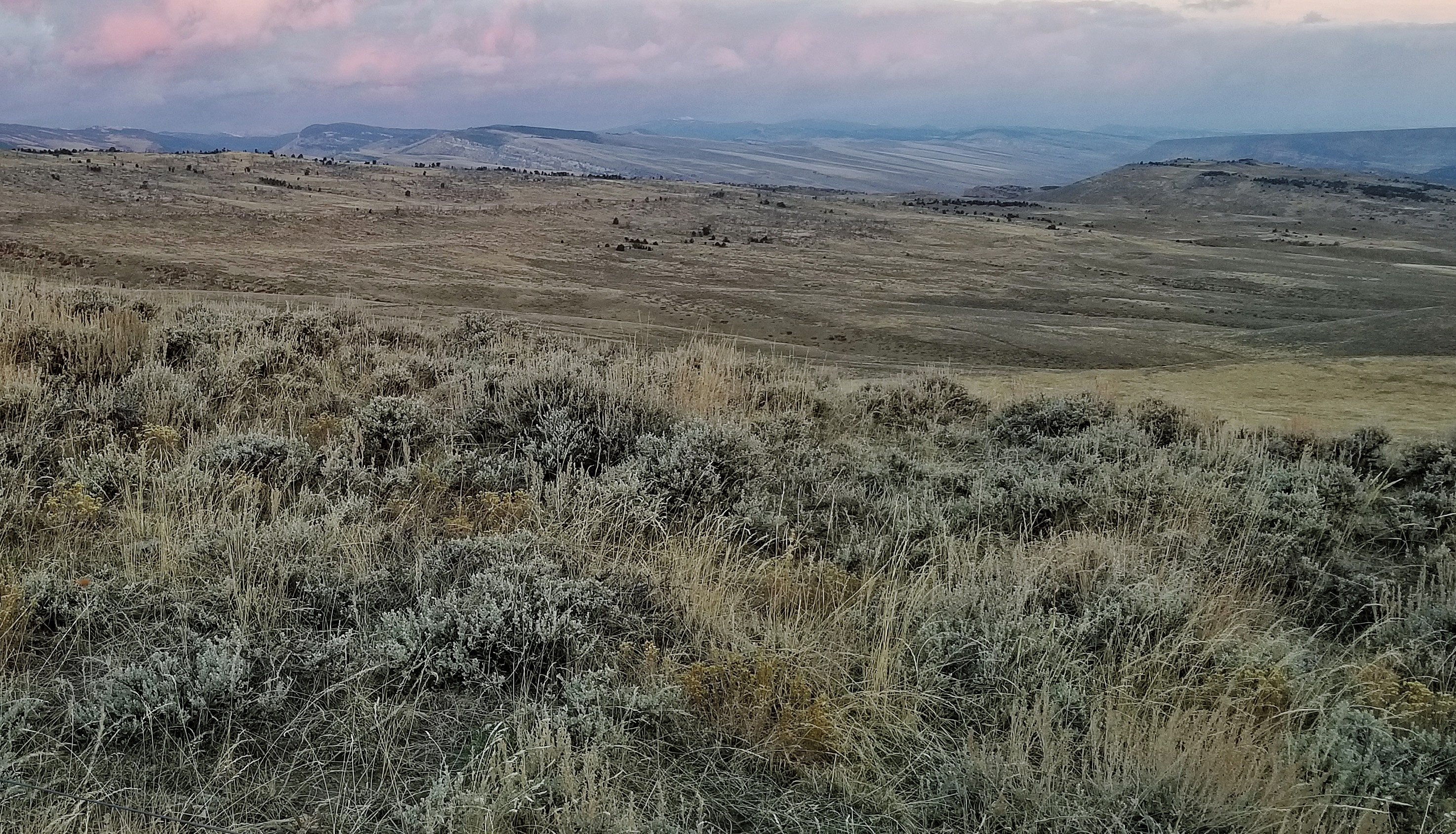
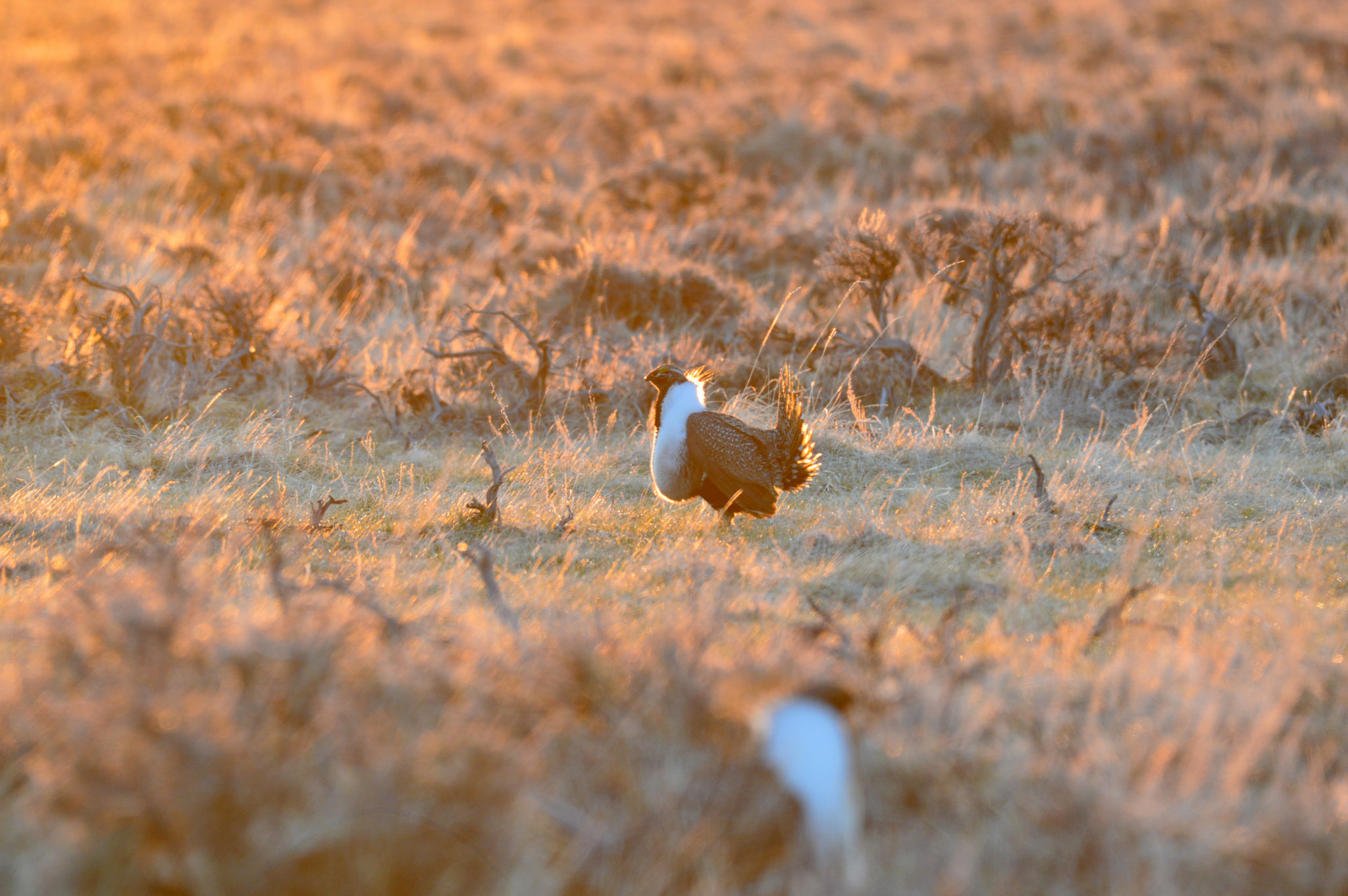
Former wildlife agency leaders, scientists, and other natural resource professionals warn that any changes to BLM’s sage grouse conservation efforts should be based on science and focused on the sagebrush habitat that supports 350 species
In a letter to Secretary Ryan Zinke, DOI staff, and the BLM today, more than 100 wildlife and natural resources professionals urged the administration to stick to the science when considering any changes to federal sage grouse conservation plans.
These professionals—each with ten to 57 years’ experience in wildlife and natural resources management, research, and conservation—came together to respond to the Bureau of Land Management’s intent to consider amending the current federal sage-grouse conservation plans finalized in the summer of 2015. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service’s landmark decision not to list greater sage grouse as threatened or endangered that same year was predicated, in part, on the effectiveness of these plans for millions of acres of the bird’s core habitat.
Many consider this to be the greatest landscape-scale conservation planning effort of modern times. “In the many years I worked as a wildlife agency director, I learned that strong cooperation between state and federal agencies is essential for successful wildlife management, and the collective compromise that kept the greater sage grouse off of the threatened and endangered species list is a shining example of wildlife management done right,” says Willie Molini, former director of the Nevada Department of Wildlife. “I believe that it would be best to let the existing sage grouse habitat plans work for a couple of years before any significant changes are considered.”
The letter asks that the plans be implemented and analyzed for effectiveness before they are altered. At the very least, the group would like to see the BLM exhaust all existing administrative methods of changing the plans before considering amendments that could delay or drastically re-chart the course for conservation. If amendments must be considered, they should be supported by science and maintain strong conservation outcomes for sage grouse. “We do not support weakening restrictions on development within priority habitat and feel any such actions would not be supported scientifically,” they write.
“We have a long way to go to keep that ‘not warranted for listing’ decision intact for sage grouse,” says Dr. Jack Connelly, a former wildlife research biologist with the Idaho Game and Fish Department, who spent most of his 41-year career working on sage grouse habitat issues. “Major changes, delays, or management actions that are not supported by the best-available science could threaten the entire conservation strategy that got us to this point—and that level of coordination and planning was an exceptional accomplishment.”
Hunting and fishing groups have been at the negotiating table in sagebrush country for years and recognize that some changes to the plans may be necessary. But a total overhaul of the plans would only serve a select few stakeholders in a diverse Western economy that has a lot riding on conservation outcomes.
“No land-use management plan—state nor federal—is perfect, so these plans should be improved upon over time,” says Dr. Ed Arnett, senior scientist for the Theodore Roosevelt Conservation Partnership. “Some changes to the plans may be acceptable right now, as long as they are science-based and don’t alter the entire course for conservation. We look forward to continuing to work with the Department of Interior and BLM to ensure sage grouse conservation is effective and also works for stakeholders across the West.”
The comment period on the BLM’s intent to consider amendments closed December 1. The agency will now begin analyzing feedback.
Read the letter from 105 wildlife and habitat experts here.
Signers include six former state agency directors, former U.S. Forest Service chiefs and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service directors, sage grouse scientists, habitat specialists, and wildlife biologists employed by state and federal agencies, universities, and non-profit conservation organizations concerned about the future of sage grouse and sagebrush conservation.
Top photo by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service via flickr.








nd I thing that the proper approach to our current administration with sound programs like the sage grouse have shown, will be favorably viewed. I lived in Jackson, Wyoming for many years and enjoyed many memorable days in the field with my pointers that I will never forget.
I wholeheartedly support continued proactive efforts to protect sage grouse and other wildlife. The Chelan Douglas Land Trust (CDLT) and I are currently working to create a 1000 acre wildlife preserve in north central Washington State in the center of what is the northern population of Washington State’s threatened sage grouse. We are currently raising funds to be able to transfer this property to the CDLT and are nearing the halfway mark in a $550,000 capital campaign. Eventually we would like to add to this preserve as opportunities allow. I’ve created a photobook of the preserve-in-the-making and would be happy to make a copy available if there is any interest out there in helping with this private/public effort to protect sage grouse in Washington State.
Thank you for the important work you are doing.
Sincerely,
Ferdi Businger
All birds should be on the Endangered Species List. SageBrush habitat Supports 350 Species of Wild life. Environment Science Supports the Sage Brush Habitat. Support the areas protecting the Environment for a clean country.
Science theory for Sage Grouse. Support the Science and the Scientist for a Clean Environment.